How to Get Baby to Change From Face Up

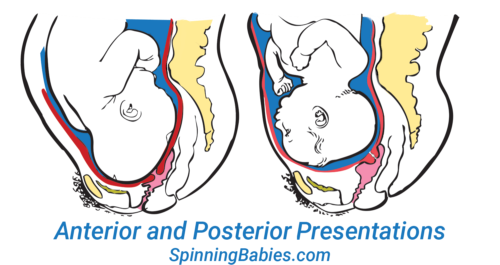
Expect at the above drawing. The posterior babe'southward back is oft extended directly or biconvex along the mother's spine. Having the baby'south back extended ofttimes pushes the baby's chin up.
Attending: Having the mentum upwardly is what makes the posterior baby'south head seem larger than the same babe when information technology's in the inductive position.
Because the top of the caput enters (or tries to enter) the pelvis showtime, infant seems much bigger by the female parent's measurements. A posterior head circumference measures larger than the anterior head circumference.
A large baby is not the aforementioned issue, however. The challenge with a posterior labor is that the top of the caput, not the crown of the caput leads the way.
A baby with their spine straight has less ability to wiggle and and so the person giving birth has to do the work of two. This can be long and challenging or fast and furious. Also, there are a few posterior labors that are not perceived different than a labor with a baby curled on the left.
Why? Anatomy makes the departure. Larn to piece of work with birth anatomy to reduce the claiming of posterior labor by preparing with our Iii Sisters of ResidualSM and more than.
What to do?
- Three BalancesSM
- Dip the Hip
- Psoas Release
- About everything on this website except Breech Tilt
In Labor, do the in a higher place and add,
- Abdominal Lift and Tuck
- Other positions to Open the Skirt
- Lunge
- Open the Outlet during pushing
There are four posterior positions
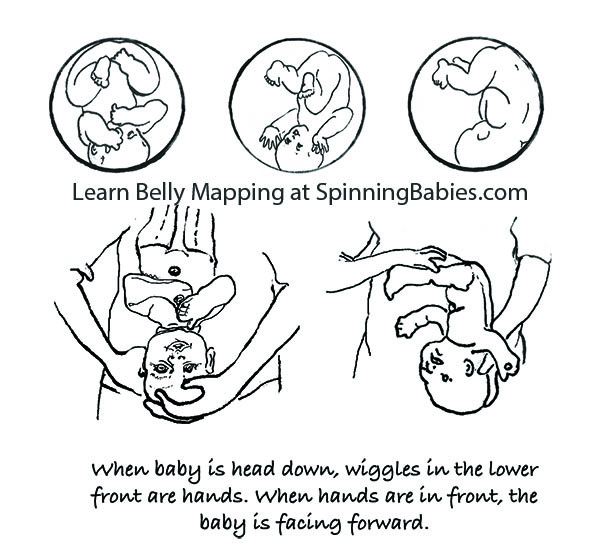
The directly OP is the archetype posterior position with the baby facing directly forrad.Right Occiput Transverse(ROT) is a mutual starting position in which the baby has a bit more likelihood of rotating to the posterior during labor than to the anterior.Right Occiput Posteriorusually involves a direct back with a lifted mentum (in the first-time female parent). Left Occiput Posterior places the baby's back opposite the maternal liver and may let the baby flex (curl) his or her back and therefore tuck the chin for a ameliorate nascence. These are generalities, of course. Run across a fleck more nigh posterior positions inBelly Mapping® on this website. Want to map your infant's position? Learn how with theBelly Mapping® Workbook.
Pregnancy may or may non testify symptoms. But considering a woman's dorsum doesn't injure in pregnancy doesn't mean the babe is not posterior. Just because a adult female is quite comfy in pregnancy doesn't mean the baby is not posterior. A adult female can't always feel the baby'due south limbs moving in front to tell if the baby is facing the front end.
The iv posterior fetal positions
Four starting positions often atomic number 82 to (or remain equally) directlyOPin active labor.Right Occiput Transverse(ROT),Right Occiput Posterior(ROP), and Left Occiput Posterior (LOP) join straight OP in calculation labor time. The LOP baby has less distance to travel to become into an LOT position.
As labor begins, the loftier-riding, unengaged Correct Occiput Transverse baby slowly rotates toROA, working past the sacral promontory at the base of the spine before swinging around to LOT to engage in the pelvis. Most babies go along to OA at the pelvic floor or further down on the perineal floor.
If a baby engages as a ROT, they may go to OP or ROA by the time they descend to the midpelvis. The OP baby may stay OP. For some, one time the head is lower than the bones and the head is visible at the perineum, the baby rotates and helpers may see the baby's caput turn then! These babies stop in the ROA or OA positions.
Feeling both hands in front, in ii carve up but low places on the abdomen, indicates a posterior fetal position. This baby is Left Occiput Posterior.
Studies estimate 15-30% of babies are OP in labor. Jean Sutton inOptimal Fetal Positioningstates that 50% of babies trend toward posterior in early labor upon access to the hospital. Potent latent labor swings nigh a third of these to LOT earlier dilation begins (in "pre-labor" or "false labor").
Recent enquiry shows about 50% of babies are in a posterior position when agile labor begins, but of these, 3/4 of them rotate to inductive (or facing a hip in an occiput transverse, head downwards position.
Jean Sutton's observations, reported in her 1996 book, indicates that some babies starting in a posterior position will rotate earlier arriving to the hospital. Ellice Lieberman observed most posteriors volition rotate out of posterior into either anterior or to facing a hip throughout labor. Only 5-8% of all babies emerge straight OP (13% with an epidural in Lieberman'due south study). At least 12% of allcesareansare for OP babies that are stuck due to the larger diameter of the OP head in comparing to the OA caput. It's more mutual for ROT, ROP, and OP babies to rotate during labor and to emerge facing back (OA). Some babies get stuck halfway through a long-arc rotation and some will need a cesarean anyway.
The iii anterior starting positions for labor
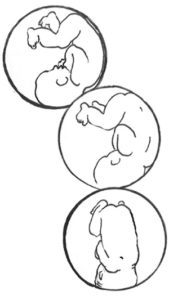 The three anteriors —LOT, LOA, and OA — are all ideal fetal positions for the start of labor. Both LOA and OA require less rotation than LOT and may lead to a faster labor, but they may also exist less common. Generally, very few midwives or doctors will pay strict attending to the actual head position, leading to the LOT babe often being referred to every bit LOA or simply OA.
The three anteriors —LOT, LOA, and OA — are all ideal fetal positions for the start of labor. Both LOA and OA require less rotation than LOT and may lead to a faster labor, but they may also exist less common. Generally, very few midwives or doctors will pay strict attending to the actual head position, leading to the LOT babe often being referred to every bit LOA or simply OA.
Why not ROA? ROA babies may have their chins up and this deflexed position may lengthen the grade of labor. Less than four% of starting positions are ROA, according to a Birmingham study. This might not be ideal for first babies, but is not a posterior position either.
The spectrum of ease across posterior labors

In that location is a spectrum of ease beyond posterior labors. Information technology'southward not a bell curve, though; easy posteriors are not as common equally challenging ones. Normally, babies turn after many strong contractions. Without help, near half of women will requite birth to their posterior babies. The techniques calledThe Fantastic Fourare likely to meliorate mothers' and babies' ease of birth! Learn these techniques that will help yous avoid unnecessary surgery for your baby's birth past watching theSpinning Babies® Parent Class video:
Parent Grade
Baby'southward posterior position may matter in labor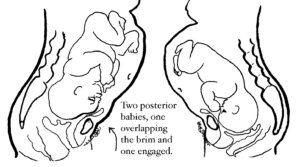
With a posterior presentation, labor may or may not be significantly afflicted. There is a spectrum of possibilities with a posterior babe. Some women will not know they had a posterior baby considering no one mentions it. Either the providers didn't know, or didn't notice. If labor moved along, they may not have looked at fetal position clues since there was no reason to figure out why labor wasn't progressing. If a woman didn't have back labor (more pain in her back than in her abdomen), the provider may not have been "clued into" baby'south position.
Some posterior babies are born in less than 8 hours and position did not ho-hum down labor. Some posterior babies are born in less than 24 hours and position did not tedious down labor plenty to be out of the norm. Some posterior babies are built-in in less than 36-48 hours without the need for interventions.
Some posterior labors are manageable when women are mobile, supported, and eat and potable freely, as needed. Some posterior labor needs extra support that a well-trained and experienced doula may provide, but that typically a mate or loved one would not take the skills or stamina to keep upwardly with. Some posterior labors progress simply with the aid of a highly-trained pregnancy bodyworker or deep spiritual, or otherwise a non-conventional model of care. Or, they seem only able to finish with medical intervention.
Some posterior labors are served by an epidural, meaning the pelvic floor relaxes enough for the baby to rotate and come up out. Some epidurals, on the other manus, go far so that a woman can not end the birth vaginally.
Notation: Parents should know — some birth researchers, like Pediatrician John Kennell, are seriously request whether a mother's epidural turns off her body'southward release of hurting-relieving hormones which a baby relies on during childbirth. Some babies tin can't turn and can't be built-in vaginally and must exist born bycesarean. This is a spectrum of possibilities. I've seen every one of the to a higher place possibilities several times and can add the wonderful experience of seeing a adult female laughing pleasurably and squatting while her posterior infant slid out on to her sleeping room floor.
Possible posterior furnishings, some women will have one or ii and some will have many of these:

The forehead that overlaps the pubic os later labor starts must turn and driblet into the pelvis to allow the birth to happen naturally. A cesarean end of the labor is possible. Await at Abdominal Elevator and Tuck in Techniques to guide you to solutions for easier appointment and progress.
- Longer pregnancy (some research shows this and some doesn't)
- The amniotic sac breaking (h2o breaks, membranes open, rupture of membranes) before labor (one in 5 OP labors)
- Non starting in fourth dimension before inductionis scheduled
- Labor is longer and stronger and less rhythmic than expected
- Offset and stoplabor pattern
- The baby may not engage, even during the pushing phase
- Longer early labor
- Longer active labor
- Dorsum labor (in some cases)
- Pitocin may be used when labor stalls (but a snoring proficient residue followed by oatmeal may restore a contraction pattern, too)
- Longer pushing stage
- Peradventure a adult female has all three phases of labor lengthened by the OP labor or one or two of the three phases listed
- Sometimes the baby's head gets stuck turned halfway to anterior – in the transverse bore. This may be chosen a transverse arrest (non atransverse lie).
- More likely to tear
- More than likely to need a vacuum (ventouse) or forceps
- More probable to demand acesarean
These effects are in comparison to a baby in theleft occiput anteriororleft occiput transversefetal position at the start of labor.
Who might accept a difficult time with a posterior baby?
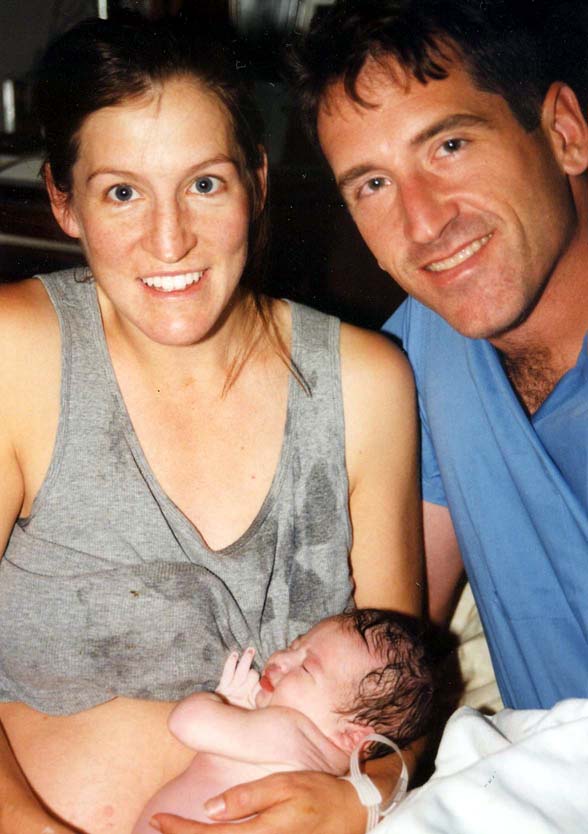

This family unit just had a fast posterior nativity of their second child! Ease in labor includes other factors beyond infant position.
- A first-time mom
- A showtime-time mom whosebaby hasn't dropped into the pelvis by 38 weeks gestation(ii weeks earlier the due date)
- A adult female with anandroid pelvis("runs like a male child," often long and lanky, low pubis with narrow pubic arch and/or sitz basic close together, closer than or equal to the width of a fist)
- A woman whose babe, in the 3rd trimester, doesn't seem to change position at all, over the weeks. He or she kicks in the womb and stretches, but whose trunk is stationary for weeks. This mother's wide ligament may be and then tight that she may be uncomfortable when baby moves.
- A woman who has an epidural early on in labor (data supports this), before the baby has a chance to rotate and come down.
- A woman who labors lying in bed
- Low-thyroid, low-free energy woman who has gone overdue (this is my observation)
- A woman who lacks support past a calm and assured woman who is calming and reassuring to the birthing female parent (a doula)
- A woman put on the clock
- A woman who refuses all help when the labor exceeds her ability to physically sustain her self (spilling ketones, aridity, unable to consume or rest in a labor over X amount of hours which might be 24 for some or 48 for others)
- A woman whose nascence team can't match an appropriate technique to the needs of the baby for flexion, rotation, and/or descent from the level of the pelvis where the babe is currently at when stuck
Who is likely to have an easy fourth dimension with a posterior infant?
- A second-fourth dimension mom who's given birth readily before (and pushing went well)
- A posterior baby with a tucked chin on his or her mama'southward left side witha round pelvic brim
- An average-sized or smaller baby
- Someone whose posterior baby changes from right to left later on doing inversions and otherbalancing piece of work, though the babe is still posterior
- A adult female with a baby in the Left Occiput Posterior, particularly if the babe'south chin is tucked or flexed
- A adult female who gets bodywork, myofascial release, etc.
- A woman whose posterior baby engages, and does non have anandroid (triangular) pelvis or a small outlet
- And of all of these, what is necessary is a pelvis big plenty to accommodate the infant's extra caput size
- A woman who uses agile birthing techniques — vertical positions, moves spontaneously and instinctively or with specific techniques from Spinning Babies®, and other expert advice
- A woman in a balanced nervous state, not so alert and "pumped upwards," on guard, etc.
Any adult female may also take an easier fourth dimension than public stance might indicate, too, just because she isn't on this list. Equally, but considering she is on the "difficult" listing doesn't mean she will accept a difficult time for sure. These are full general observations. They are neither condemnations nor promises. Overall, some posterior babies will demand help getting built-in, while some posterior babies are born hands (easy being a relative term).
Permit's not be ideological about posterior labors.
While most posterior babies do eventually rotate, that can yet hateful there is quite a long wait – and a lot of physical labor during that wait. Sometimes it ways the doula, midwife, nurse, or doctor is asking the mother to do a variety of position changes, techniques, and even medical interventions to aid finish the labor. Patience works for many, but for some acesareanis really the only way to be born. ReadWhat To Do When…in Labor.
What causes a baby to be posterior?
There is a rise incidence of posterior babies at the fourth dimension of nascence. We know now that epidural anesthesia increases the rate of posterior position at the fourth dimension of birth from about 4% (for women who don't choose an epidural in a academy birth setting) up to about 13% (Lieberman, 2005). Low thyroid part is associated with fetal malposition such equally posterior or breech. (SeeResearch & References.)
Most babies who are posterior early on in labor will rotate to anterior once labor gets going. Some babies rotate late in labor, even merely earlier emerging. Studies such every bit Lieberman'southward show that at whatever given phase of labor, another 20% of posterior babies will rotate and so that simply a small number are yet posterior as the head emerges.
My observations are that the bulk of babies are posterior before labor. The high numbers of posterior babies at the stop of pregnancy and in the early on phase of labor is a change from what was seen in studies over ten years old. Possibly this is from our cultural habits of sitting at desks, sitting in saucepan seats (cars), and leaning back on the burrow (slouching). Soft tissues such as the psoas muscle pair or the broad ligament also seem to be tight more often from these postures, from athletics (quick stops, jolts, and falls), from accidents, and from emotional or sexual assail.
Being a nurse or bodyworker who turns to care for people in a bed or on a tabular array volition also twist the lower uterine segment (along with some of the previously mentioned causes). This makes the baby take to compensate in a womb that is no longer symmetrical. Less often, the growing baby settles face up-forrad over a smaller pelvis, or a triangular-shaped pelvis (android). At the end of pregnancy, the baby's forehead has settled onto a narrower than usual pubic bone, and if tight round ligaments hold the brow in that location, the baby may have a tough time rotating. These are the moms and babies that I'm almost concerned with in my work at Spinning Babies®. A baby that wasbreechbeyond week 30 – 34 of pregnancy will flip head down in the posterior position. A woman with a history of breech or posterior babies is more than probable to have a breech or posterior infant in the next pregnancy. However, she may non have an as long labor.
The all-time way to tell if your baby is OP or not, usually, is if yous feel piddling wiggles in the abdomen right in a higher place your pubic bone. These are the fingers. They'd feel like footling fingers wiggling, not like a big thunk or grinding from the head, though yous might experience that, too. The little fingers will be playing by the mouth. This is the easiest indication of OP. The wiggles will be centered in the heart of your lower abdomen, close to the pubic bone. If you feel wiggles far to the right, most your hip, and kicks in a higher place on the correct, but non near the center and none on the left, then those betoken anOAorLOTbaby (who will rotate to the OA hands in an active birth). After this, yous might go toWhat to practice when…in Labor.
Check out our electric current references in the Research & References section.
Videos
Daily Essentials
Daily Essentials can exist practiced daily throughout pregnancy to assistance bring balance and comfort — and an easier, shorter birth.
Spinning Babies® Parent Class
Spinning Babies® Parent Class provides clear instructions on how to use Spinning Babies® for a more comfortable and confident pregnancy and labor.
How to Get Baby to Change From Face Up
Source: https://www.spinningbabies.com/pregnancy-birth/baby-position/posterior/
 What is a posterior fetal presentation? The baby's dorsum is spine-to-spine with the mother.
What is a posterior fetal presentation? The baby's dorsum is spine-to-spine with the mother.


0 Response to "How to Get Baby to Change From Face Up"
Post a Comment